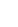
Ok, this is a bit of a play on the famous saying that all of us are connected by 6 degrees of separation, or in the case of Hollywood, “6 degrees of Kevin Bacon.” In this case, we are more referring to the various steps that are between you and your data in the world of IoT.
Starting from your device in the field:
Information gathering
This can vary based on upon what/where you are looking to gather information from. For instance, your device may have the ability to provide you with all of the valuable data that you wish to know simply by plugging in a cable or connecting it to your Wi-Fi network. On the other hand, if you are looking to know the temperature of a room, it may involve using a simple sensor.
Local Area Network
Once you have the data, it needs to be transported. The first step to doing that is to move it from the device to your gateway. This may be done using a cable, Wi-Fi or a more IoT-focused network like LoRa or Bluetooth.
Edge Devices
All of your information that you have gathered now has to be sent up to your application. This usually happens at your edge device. It may be a simple router/gateway, like those used in home applications or a more complex one that is capable of performing advanced functions at the site.
Wide Area Network
The information now needs to make its way from your location up to your server to be processed. In most cases, this involves using a Wide Area network. This may use an existing landline network that you have, use a cellular-based network or if you are more remote, may use a satellite or Private radio network to make its journey.
IoT Application
Now that your data has been received, it needs to be put into your application. More and more, these applications are hosted in the cloud, but some organizations still host their own data servers. The application will take this information and start to make it more useful for the user.
End user experience
Once the data has been processed by the application, it needs to be shown to the user in a manner that they find useful. It may be in the form of a text message to alert to a critical situation, a graph that allows a user to see historical changes or it may be used in a financial application to better project expenses.
During each step of the way, there are two important things that must be accounted for. The first is device management. If any piece of hardware is not available, the chain breaks and you are not connecting to your remote devices. Device management can be done via your hardware provider’s platform and/or by your IoT application.
As important as keeping devices up and running is, keeping your data secure is equally important. Many different technologies help to keep your data safe; passwords to access your portal and devices, encryption of data being sent across networks and biometrics to control access to end-user devices are a few key ones.
If you are more of a visual kind of person, here is a graphic to help: